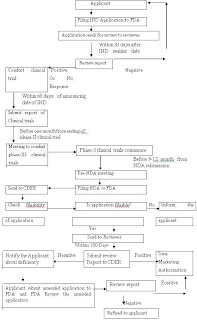
 IND-Investigational New Drug, FDA-Food and Drug Administration, NDA-New Drug Application, CDER-Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research
IND-Investigational New Drug, FDA-Food and Drug Administration, NDA-New Drug Application, CDER-Centre for Drug Evaluation and ResearchTable 1. Comparison of Drug approval process.
| Country | Time for Regulatory Approval of CTA/IND Application | Time for Evaluation of MAA | MAA Fee |
| Australia | 120 day | 50 days | $192,400 |
| China | 50 days | 180 days | DNA |
| India | 16-18 weeks | 8-12 weeks | 50,000 INR |
| UK* | 35 days | 210 days | £254100 |
| USA | 30 days | 180 days | $217,787 |
Figure 1: New Drug Application Approval Process of FDA
Figure 2: Clinical Trial Authorization Process of EU
MAA-Marketing Authorization Application, EMEA-European Medicine Evaluation Agency, EU-European Unionion in EU
Figure 3:Centralized Procedure for Marketing Authorizat
CMS(s)-Concerned Member State(s), RMS-Reference Member State, CHMP-Committee for Human Medicinal Products
Figure 4: Decentralised Procedure for Marketing Authorization in EU
CDE-Centre for Drug Evaluation, SFDA-State Food and Drug Administration



